What is Identity and Access Management?
Authenticate who has access to what
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a security practice and business discipline that involves a combination of technologies and processes to ensure that the right users and machines have access to the right assets, while keeping fraudsters out.
IAM frameworks enable organizations to define user roles or group identities within their cloud infrastructure. Typically, IAM policies are formatted as text files containing identity and permission rules. For example, a team may allow a group of users to upload files to a specific location—but in real-world scenarios, organizations often manage hundreds or thousands of IAM policies.
Importance of IAM
IAM enables organizations to authenticate users and grant access only to necessary assets. Without IAM, it would be extremely difficult to manage access at scale or ensure secure collaboration.
If every user had the same level of access, it would expose the organization to serious security risks. Why should developers working on finance systems have the same access as those on HR teams?
Benefits of a strong IAM structure:
- Improved Security: Know who has access to what to prevent unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Align with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and more.
- Increased Productivity: Reduce interruptions by ensuring focused access.
- Cost Optimization: Streamlined access reduces operational inefficiencies.
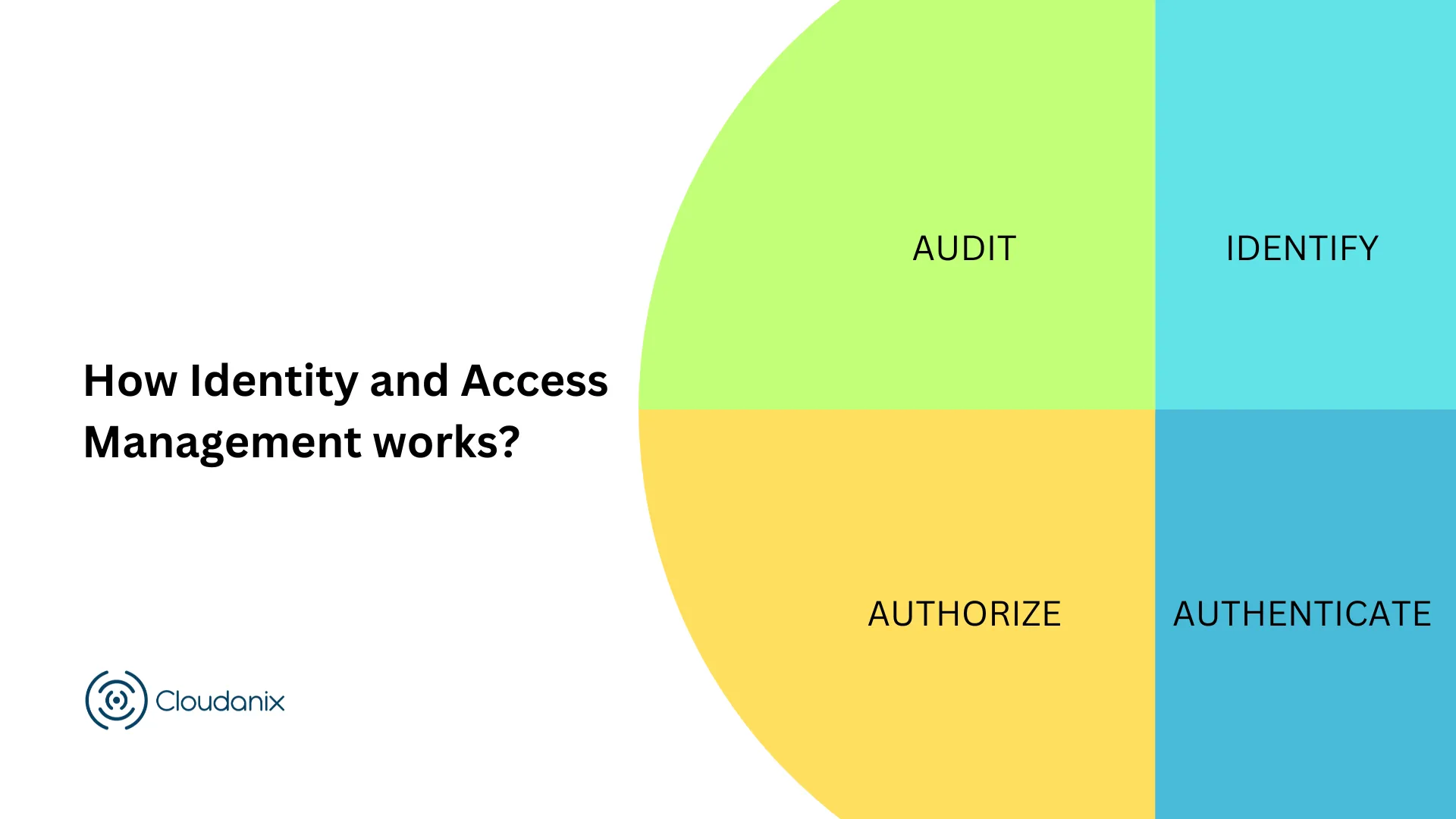
How IAM Works
IAM consists of four fundamental processes:
- Identify – Use usernames, passwords, user roles, and attributes.
- Authenticate – Validate user credentials (e.g., password + MFA).
- Authorize – Grant access only to required resources.
- Audit – Track who accessed what, when, and what actions were taken.
Learn how Cloudanix CIEM helps simplify this: Cloud Compliance | CIEM | Cloudanix
Identity Management vs Access Management
Identity Management:
Manages digital identities across cloud and on-prem environments. It includes provisioning, updating, and deactivating user accounts securely.
Access Management:
Controls what each identity can access based on policies. Enables scalability, simplicity, and security in cloud-based operations.
Why Organizations Need IAM
Over 80% of data breaches occur due to IAM misconfigurations.
IAM is a pillar of cloud security, reducing internal missteps and securing sensitive assets. It ensures compliance and enables organizations to confidently pass audits.
IAM and Regulatory Compliance
IAM plays a key role in maintaining compliance with:
- GDPR
- HIPAA
- PCI-DSS
- SOC 2
- and many other regional and industry-specific regulations
Insufficient IAM documentation can fail audits—even if other security layers are strong.
Additional Benefits of IAM
- Automation: Onboarding and offboarding users with ease.
- Anomaly Detection: Spot suspicious access behavior early.
- Enable Zero Trust: Enforce “never trust, always verify” at every layer.
- Mitigate Insider Threats: Secure access not only for employees but also contractors, clients, and partners.
Implementing IAM
Before rolling out IAM, determine who owns its governance. Your IAM team should include representatives from IT, security, HR, and business operations.
Recommended steps:
- Make a list of applications and components users will interact with.
- Understand your cloud and on-premise architecture.
- Identify critical IAM features (e.g., MFA, SSO, privilege boundaries).
- Centralize your identity systems and adopt best practices.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of IAM regularly and scale based on findings.
IAM for Security Professionals
Cloudanix provides a central dashboard to manage IAM misconfigurations, monitor access boundaries, and enforce JIT access across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
IAM Tools You Should Know
MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication)
A process that requires multiple forms of identification—e.g., password + OTP or fingerprint.
How to set up MFA devices in AWS - Read the blog
SSO (Single Sign-On)
SSO allows users to log in once and access multiple applications seamlessly.
Developer’s guide to SSO for enterprise apps - Read the blog
Know Your Identities - IAM Audits
Your data deserves the highest level of protection.
Let me know if you’d like to break this up into smaller files or pages (e.g., IAM Overview, IAM Best Practices, IAM Compliance).
