Secret scanning, at its core, is the process of automatically detecting and identifying sensitive information, or “secrets,” that have been unintentionally exposed within code repositories, configuration files, logs, and other digital assets.
Secret scanning was introduced to address the escalating problem of unintentionally exposed sensitive credentials within code and configurations. It’s a direct response to the increasing frequency of breaches caused by hardcoded API keys, passwords, and other secrets leaking into version control systems and cloud environments. Essentially, it automates the detection of these exposures, shifting security left in the development lifecycle and mitigating the risk of widespread compromise.
These secrets, such as API keys, passwords, and cryptographic keys, pose significant security risks if exposed. Secret scanning tools employ techniques like pattern matching, entropy analysis, and contextual analysis to detect these secrets. Integrated into the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC), it scans code pre-commit, during CI/CD pipelines, and within repositories. The goal is to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and financial losses by proactively detecting and remediating exposed credentials, thereby strengthening an organization’s overall security posture.
What Are Secrets?
In the context of secret scanning, “secrets” refer to any sensitive pieces of information that, if exposed, could compromise the security of systems, applications, or data. They are credentials and keys used for authentication, authorization, and encryption. To make it more consumable, here is a breakdown:
- Authentication Credentials: These are used to verify the identity of users or systems. Examples include passwords, API keys, access tokens, and SSH private keys.
- Authorization Credentials: These determine the level of access granted to a user or system. Examples include API keys with specific permissions, service account keys, and database credentials.
- Encryption Keys: These are used to encrypt and decrypt data, ensuring its confidentiality. Examples include private keys for SSL/TLS certificates, symmetric encryption keys, and asymmetric key pairs.
- Configuration Secrets: These are sensitive configuration data, such as database connection strings, cloud provider access keys, and other parameters that should not be publicly exposed.
Essentially, secrets are any data that should be kept confidential to prevent unauthorized access and maintain the security of systems and data.
Difference Between Secrets And Sensitive Data
The main difference between secrets and sensitive data can be explained as follows:
- Secrets are credentials (like API keys, and passwords) that grant access. Secret scanning finds these to prevent unauthorized entry.
- Sensitive Data is the information being protected (like customer records, and financial data). Secret scanning helps prevent the exposure of the credentials that could lead to this data being accessed.
The examples of secrets are:
- API Keys (e.g., for cloud services, payment gateways)
- Database Credentials (usernames and passwords)
- Private SSH Keys
- TLS/SSL Certificates (private keys)
- Cloud Provider Access Keys/Tokens (AWS access keys, Azure service principal secrets, GCP service account keys)
What is it - Secret Scanning or Secret Detection?
Often these terms (Secret scanning and Secret detection) are used interchangeably. But, there’s a subtle and important distinction between both of them. Particularly in how they’re applied and the scope they encompass.
- Secret Detection: This term generally refers to the process of identifying potential secrets within a given dataset. It’s the core technical function of analyzing code, configurations, or other files to locate strings that match patterns or exhibit characteristics of secrets.
- Secret Scanning: This term implies a broader, more holistic security practice. It encompasses not only the detection of secrets but also the subsequent actions taken. Scanning is the application of the detection process in a security context. It focuses on the “what” and the “how” – finding secrets and managing the risk.
We hope after reading the above-mentioned details, we have set our stage to understand our topic “Secret Scanning” in detail. Let us dive into it.
How does secret scanning work?
Imagine secret scanning as a highly efficient security guard constantly patrolling your digital environments. Now, let us break down clearly and concisely how secret scanning works:
Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
The process begins by gathering the data to be scanned. This could be code repositories (Git, SVN, etc.), configuration files (YAML, JSON), cloud storage buckets, container images, or even log files. The data is then preprocessed to normalize it and make it easier to analyze. This generally involves:
- Extracting text from files.
- Decoding encoded data (e.g., Base64).
- Tokenizing the text (breaking it into smaller units).
Pattern Matching (Regular Expressions)
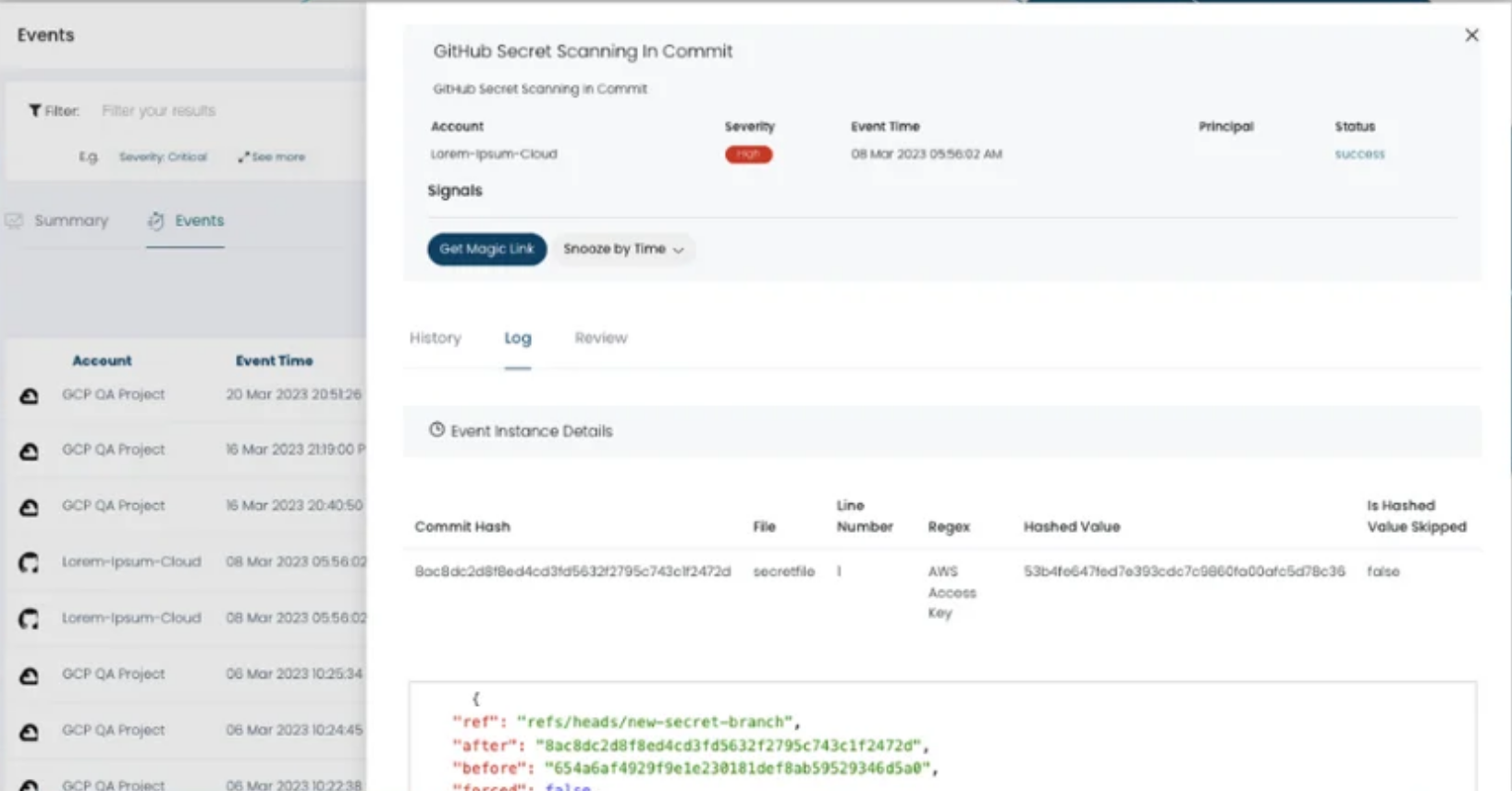
A core component of secret scanning is the use of regular expressions (regex). These are powerful search patterns that can identify strings matching known formats of secrets. For example, there are regex patterns specifically designed to identify AWS access keys, API keys from various providers, or common password formats. The scanning engine compares the preprocessed data against these regex patterns. When a match is found, it’s flagged as a potential secret.
Entropy Analysis
Many secrets, especially cryptographic keys and tokens, exhibit high entropy (randomness). Entropy analysis calculates the randomness of a string. Strings with high entropy are more likely to be secrets. This technique is particularly useful for detecting secrets that don’t have easily recognizable patterns.
Contextual Analysis
Simply finding a string that matches a pattern or has high entropy isn’t enough. It’s crucial to analyze the context in which the string appears. Contextual analysis involves examining the surrounding code or text to determine if the potential secret is being used sensitively. For instance, a string might be flagged as a potential API key, but if it’s found in a comment or a test file, it might not be a real risk. However, if it is used in a network request, it is of much higher risk.
Validation (API Checks)
Some secret scanning tools (e.g. Cloudanix) go a step further and attempt to validate potential secrets. For example, if a potential API key is found, the tool might try to use it to request the corresponding API endpoint. This helps to confirm whether the key is valid and active.
Reporting and Remediation
Once the scanning process is complete, the tool generates a report listing all the detected secrets. This report typically includes information about the location, types, and risk severity of the secret. The security team then uses this report to remediate the exposed secrets. This might involve:
- Revoking the exposed keys or tokens.
- Rotating passwords.
- Removing the secrets from the codebase.
- Implementing better secret management practices.
Integration and Automation
To be effective, secret scanning needs to be integrated into the development workflow. This can be done by:
- Running scans as part of CI/CD pipelines.
- Using pre-commit hooks to scan code before it’s committed.
- Regularly scanning existing repositories.
In essence, secret scanning automates the critical task of finding exposed credentials, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers and strengthening an organization’s security posture by proactively addressing potential breaches before they occur.
What are the different secret scanning techniques used?
We have tried to explain the secret scanning techniques that industries today rely on. This list was built on the working principles we just discussed above:
Regular Expression (Regex) Matching
This is the most common technique, using predefined patterns to identify known secret formats. Industries use extensive regex libraries that are regularly updated to catch new secret patterns from various vendors and services. It’s fast and efficient for known patterns, but less effective against obfuscated or unknown secret formats.
Entropy Analysis
This technique measures the randomness of a string. Cryptographic keys and tokens typically have high entropy. Industries use this to detect secrets that might not match known regex patterns. It’s particularly useful for detecting randomly generated secrets, but can also produce false positives with other high-entropy data.
Contextual Analysis (Heuristics)
This goes beyond simple pattern matching by analyzing the surrounding code or configuration to determine if a potential secret is being used in a sensitive context. Industries use this to reduce false positives by understanding how a string is used. For example, a string that looks like an API key in a test file might be ignored, while the same string in a network request would be flagged. This technique often involves machine learning to improve accuracy.
API Validation (Active Scanning)
This technique actively attempts to validate potential secrets against known API endpoints. Industries use this to confirm if a detected secret is valid and active. This is highly effective but can be resource-intensive and potentially trigger security alerts on the target APIs. It’s often used for critical systems and high-risk secrets.
Dictionary Attacks (Keyword Scanning)
While not as common as regex, this technique uses dictionaries of common secret names or keywords (e.g., “password,” “api_key,” “secret”) to search for potential secrets. Combined with contextual analysis, this can uncover secrets that might be missed by other techniques. It’s often used in conjunction with other methods to improve coverage.
Git History Scanning
This technique specifically scans the entire Git history of a repository, including past commits, to detect secrets that may have been accidentally committed and then removed. Industries use this to ensure that even deleted secrets are identified and remediated. This is crucial for preventing attackers from accessing secrets that were once present in the repository.
SAST Integration (Static Application Security Testing)
Integrating secret scanning into SAST tools allows for deeper code analysis and better contextual understanding of potential secrets. Industries use this to identify secrets within the application’s source code, configuration files, and dependencies during the development phase. This allows for early detection and remediation of secrets.
Secret Management Integration
Integrating secret scanning with secret management solutions (like HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager) allows for automated rotation and replacement of detected secrets. Industries use this to streamline remediation and improve overall secret management practices. This ensures that detected secrets are not only found but also properly managed.
In practice, the most effective secret scanning strategies leverage a combination of these techniques, tailoring their approach to the specific risks and requirements of their environment. This layered approach ensures comprehensive coverage and minimizes the likelihood of exposed secrets slipping through the cracks.
What is the importance of secret scanning?
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, secrets are the keys to the kingdom. If these keys are left lying around, the kingdom is vulnerable. This is precisely where secret scanning steps in as a critical security component. Let us explore the profound importance of secret scanning, emphasizing its role in modern security practices:
- Preventing Catastrophic Data Breaches: Exposed secrets, like API keys or database credentials, provide a direct path for attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. In an era of increasing data breaches, secret scanning acts as a proactive defense, identifying and mitigating these vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This helps prevent large-scale data leaks, protecting sensitive customer information, financial data, and intellectual property.
- Mitigating the Impact of Insider Threats: Whether intentional or accidental, insider threats can lead to significant security breaches. Secret scanning helps detect secrets that may have been inadvertently exposed by employees or contractors, reducing the risk of data exfiltration or unauthorized access. It also helps detect intentional internal data theft.
- Enhancing Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding data protection and privacy. Secret scanning helps organizations demonstrate compliance by proactively identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities. It provides an audit trail of detected secrets and remediation efforts, which can be crucial for regulatory audits.
- Strengthening Supply Chain Security: Software supply chains are increasingly complex, involving numerous third-party dependencies. Secret scanning helps identify secrets that may have been exposed in third-party libraries or components, reducing the risk of supply chain attacks. This is especially important as organizations rely on more and more open-source code.
- Accelerating Incident Response: In the event of a security incident, rapid detection and remediation are crucial. Secret scanning provides real-time alerts when secrets are detected, enabling security teams to quickly respond and contain the damage. It also provides valuable forensic information for incident investigation.
- Shifting Security Left in the Development Lifecycle: Integrating secret scanning into the CI/CD pipeline allows for the early detection of secrets during the development process. This “shift left” approach helps prevent secrets from reaching production environments, reducing the cost and complexity of remediation.
- Protecting Cloud Environments: Cloud environments, with their dynamic nature and numerous services, are particularly vulnerable to secret exposure. Secret scanning helps protect cloud resources by identifying and mitigating exposed cloud provider credentials, API keys, and other secrets.
- Automating Security and Reducing Human Error: Manual secret detection is time-consuming and prone to human error. Secret scanning automates the process, providing continuous monitoring and reducing the risk of missed vulnerabilities.
In a world where secrets are constantly at risk, secret scanning is the essential practice that provides the necessary security vigilance required to protect your organization.
Where to scan for secrets?
In the relentless pursuit of robust security, organizations must prioritize proactive secret scanning. Focusing on areas where secrets are most likely to reside is paramount. Here are three key locations for secret scanning that organizations consistently find valuable:
Version Control Systems (VCS) - Git Repositories
Git repositories, especially public ones, are a goldmine for exposed secrets. Developers often accidentally commit sensitive information directly into their code or configuration files. Scanning the entire commit history, including past commits and branches, is crucial. This is because even if a secret is later removed, it may still exist in the repository’s history.
VCS platforms are the primary storage for source code, making them a central point of failure if secrets are leaked. Automated scanning of these systems can quickly identify and remediate exposed credentials, minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Pipelines
CI/CD pipelines automate the build, test, and deployment of applications. These pipelines often involve the use of secrets for tasks like accessing databases, deploying to cloud environments, or integrating with third-party services. Scanning these pipelines for exposed secrets is essential, as they are a direct pathway to production environments.
Integrating secret scanning into CI/CD pipelines allows for early detection of secrets during the development process. This “shift left” approach prevents secrets from reaching production, reducing the risk of security breaches. Additionally, automated scanning ensures that every build and deployment is checked for exposed secrets.
Cloud Configuration and Storage (e.g., AWS S3 Buckets, Azure Blob Storage)
Cloud storage services often contain configuration files, logs, and other sensitive data. Misconfigurations or accidental public exposure of these storage locations can lead to the leakage of secrets. Scanning these cloud storage locations for exposed credentials is crucial for protecting cloud resources.
Cloud environments are dynamic and complex, making manual inspection challenging. Automated scanning of cloud storage ensures that secrets are continuously monitored and protected. This is particularly important for organizations that rely heavily on cloud services and store sensitive data in cloud storage.
By diligently scanning these three core areas, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface and minimize the risk of devastating secret exposures.
What are the 4 proven ways to automate secret scanning?
Automating secret scanning is crucial for continuous security monitoring and proactive risk mitigation. By integrating these strategies into your workflows, organizations can ensure consistent and efficient detection of exposed credentials, regardless of their size.
Integrate Secret Scanning into CI/CD Pipelines
Embed secret scanning tools directly into your CI/CD pipelines. This ensures that every code commit and deployment is automatically scanned for secrets. If a secret is detected, the build or deployment process is halted, preventing the secret from reaching production.
This “shift-left” approach catches secrets early in the development lifecycle, reducing the cost and complexity of remediation. It also promotes a culture of security awareness among developers.
Use pipeline orchestration tools (like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and GitHub Actions) to trigger secret scanning tools as part of the build process.
Automate Git History Scanning with Scheduled Tasks
Git history is a common source of exposed secrets. Automated scanning ensures that no secret goes undetected, even if it was accidentally committed and later removed.
Use scripting languages (like Python) and Git command-line tools to automate the scanning process. Schedule these scripts to run periodically using task schedulers (like cron or Windows Task Scheduler).
Leverage Pre-Commit Hooks for Developer Workstations
Implement pre-commit hooks that scan code for secrets before it’s committed to the repository. This provides immediate feedback to developers and prevents secrets from being committed in the first place.
Pre-commit hooks empower developers to take ownership of security and prevent secrets from entering the codebase. It also provides immediate feedback to the developer.
Use Git’s built-in pre-commit hook functionality and integrate secret scanning tools into these hooks.
Automate Cloud Configuration Scanning with Cloud Provider APIs
Cloud environments are dynamic and complex, making manual inspection challenging. Automated scanning ensures continuous monitoring and protects cloud resources from misconfigurations and accidental exposures.
Use cloud provider SDKs or CLI tools to access configuration data and integrate secret scanning tools into automated scripts. Schedule these scripts to run periodically using cloud-native scheduling services (like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions).
Automation not only improves efficiency but also ensures consistency and reduces the risk of human error, making secret scanning a seamless part of the security workflow.
How can Cloudanix help in your Secret Scanning journey?
Cloudanix streamlines your secret scanning journey by providing a high-speed, comprehensive, and automated defense layer for your Software Configuration Management (SCM) platforms. By integrating Cloudanix, organizations can shift security left and proactively manage the risk of exposed credentials through the following specialized capabilities:
- Extensive Pattern Detection
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
- Customizable Security
- Comprehensive SCM Visibility
- Seamless One-Click Integration
- Secrets Verification
