Most of us have witnessed the transition of how software development has evolved from traditional project management processes to agile and DevSecOps. And now, with AI impacting every other field, the impact on the software development field was like an atom gaining an electron to convert itself into an ion.
We cannot deny the fact that the use of AI has empowered development teams and helped them build things at great speed and autonomy. However, when you look at it from a security leader’s perspective, understanding how AI models generate code is crucial. The AI-generated code often lacks explainability. This type of code creates varied vulnerabilities, resulting in complex environments that are nearly impossible to resolve.
Not just AI, but using code from open source without due diligence is also the reason that vulnerabilities may enter your systems.
What is Vulnerability Prioritization?
No doubt that organizational assets contain a diverse set of vulnerabilities that you (security professionals) cannot turn your eyes from. But what exactly to look upon?
Vulnerability prioritization tackles this challenge by providing a systematic approach for evaluating and ranking identified vulnerabilities. It considers factors like the potential impact of an exploit, the ease of exploitation, and the criticality of the affected assets.
Prioritizing vulnerabilities helps organizations and their security teams maintain their optimum level of security posture. They can do this by focusing their resources (mostly limited) on addressing the most critical risks first, reducing the likelihood of a successful attack and minimizing potential damage.
Is vulnerability prioritization important?
Learnings from the above section might have given you a decent understanding of the challenges of vulnerabilities in an active system. Thus, Vulnerability prioritization emerges as a critical function to invest in!
Vulnerability prioritization provides a structured approach to analyzing and ranking vulnerabilities. Considering factors like exploitability, potential impact, and the importance of affected assets, organizations can identify the most painful threats first. Following this practice enables organizations to strategically allocate their security resources, focusing on the vulnerabilities with the highest potential for causing significant damage. Without prioritization, security efforts may go unnoticed, and organizations continue to exploit vulnerabilities.
A comprehensive tool like Cloudanix strategically aligns with your SDLC and notifies you every time a misconfiguration has occurred in your cloud environment.
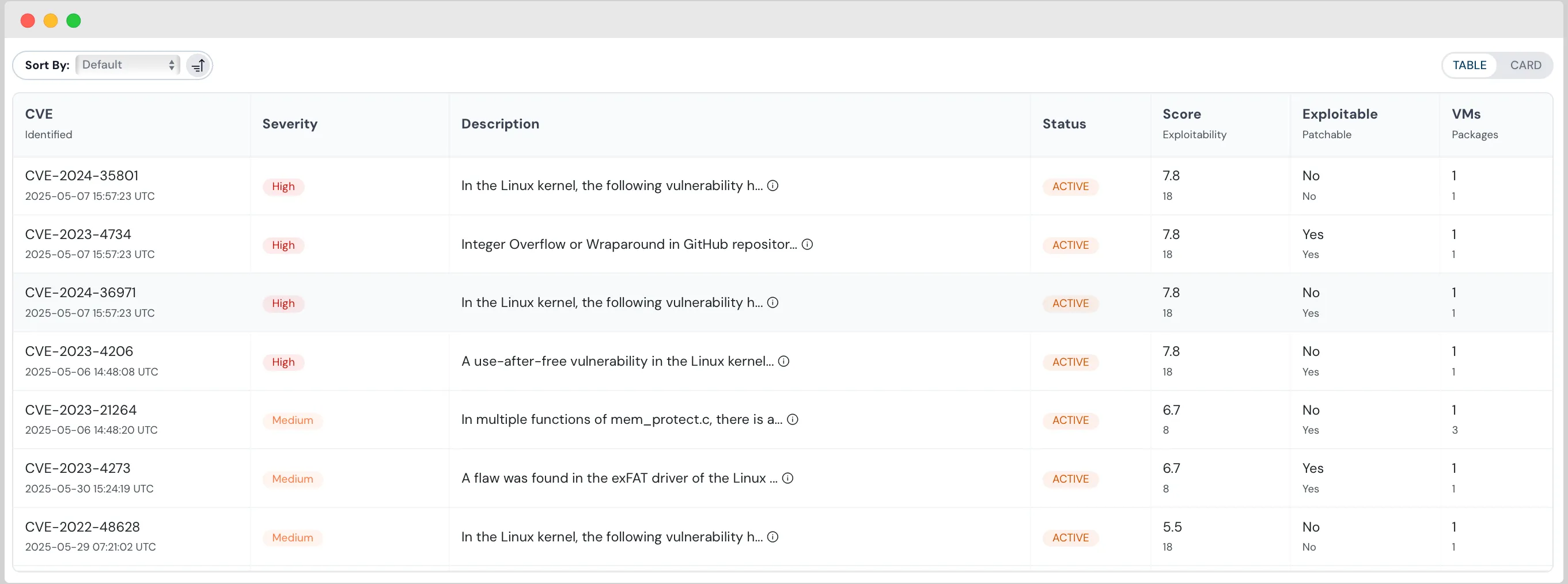
What are the most common vulnerability prioritization methods?
Now that we know the importance of vulnerability prioritization and its impact on business goals, including the relief it provides to security teams. We have listed some of the most common vulnerability prioritization methods that are worth investing your time and effort in. Let us understand them each.
CVSS scoring
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) assigns a numerical score (0-10) reflecting the overall severity of a vulnerability. It considers exploitability, impact, and scope, providing a standardized baseline for prioritization and decision-making. Higher scores indicate more critical vulnerabilities requiring immediate attention.
Exploit availability and threat intelligence
Consider the availability of working exploits for the specific vulnerability. Threat intelligence feeds can provide insights into attacker trends and the likelihood of a particular vulnerability being actively exploited. Focus on vulnerabilities with readily available exploits and those aligned with known attacker behaviors.
Business context and asset criticality
Not all systems or data have the same value within an organization. Prioritize vulnerabilities that expose critical assets, such as customer databases, financial systems, or intellectual property. Consider the potential business impact of a successful exploit, such as financial losses, reputational damage, or operational disruptions.
Don’t prioritize vulnerabilities in isolation. Consider the vulnerability’s relevance to specific business functions. For example, a vulnerability in a rarely used marketing tool might have a lower business risk compared to one in your application or a platform.
Age of vulnerability
“Zero-day” vulnerabilities, previously unknown and unpatched, often pose a higher risk as there are no existing defenses. Prioritize recently discovered vulnerabilities over older ones, especially if they have publicly available exploit details.
Ease of remediation
The effort required to fix a vulnerability can also influence prioritization. While critical vulnerabilities should be addressed regardless of difficulty, consider the complexity of remediation when dealing with vulnerabilities of similar severity. Easier to fix vulnerabilities that can be addressed more quickly, potentially freeing up resources to tackle more complex issues later.
Create a matrix with likelihood (e.g., high, medium, low) of an exploit on one axis and impact severity (e.g., high, medium, low) on the other. Place vulnerabilities based on their assessed likelihood and potential impact. Focus on those falling in the “high likelihood, high impact” quadrant first.
This one is the bonus - Attack trees
These visual representations map out potential attack scenarios and their impact. By analyzing attack trees, organizations can identify vulnerabilities that form critical nodes within the attack path, allowing them to prioritize weaknesses that would significantly disrupt the attacker’s progress.
Additionally, you may want to consider assessing your software security risks based on OWASP’s Top Web Application Security Risks.
What are the challenges of vulnerability management?
Security leaders can understand the importance of collaboration with different teams within the organization. Effective vulnerability prioritization requires collaboration primarily between engineering and business teams. However, each side can face unique challenges. We have explained a list of challenges that we have identified over the years.
Technical complexity
Translating technical complexities into actionable risk insights for business stakeholders is often a significant pain that engineers face. Explaining exploitability or potential impact in a way that resonates with business needs can be difficult.
False positives and negatives
Security scanners can generate false positives (flagging non-critical issues) or negatives (missing real vulnerabilities). Engineers need to invest time in validating vulnerabilities and ensuring prioritization reflects true risks.
Remediation effort
Engineers understand the complexities of patching and remediation. A vulnerability might be technically critical and can require significant resources to fix. Prioritization needs to consider the feasibility and effort involved in remediation alongside the risk itself.
Incomplete information
While this is not an engineering-led challenge, but more of a business-led challenge. Business stakeholders might not fully grasp the potential consequences of security vulnerabilities. Translating technical risk into business impact (e.g., lost revenue, reputational damage) is crucial for securing buy-in for prioritization efforts.
Short-term vs. Long-term focus
Business leaders might prioritize immediate concerns over long-term security risks. Shifting focus towards proactive security investments and understanding the potential long-term costs of breaches is crucial.
Cost vs. Risk trade-offs
Remediation and security controls come at a cost. Balancing the financial impact of controls with the potential risks of vulnerabilities requires clear communication and collaborative decision-making.
Compliance vs. Security
Organizations might prioritize compliance with regulations over addressing critical vulnerabilities unrelated to specific regulations. Keeping a balance between meeting compliance requirements and proactively addressing broader security risks is essential.
Data Overload and Limited Resources
Business stakeholders might be overwhelmed by the sheer volume of vulnerability data. Security teams need to effectively communicate prioritized risks clearly and concisely to facilitate informed decision-making within resource constraints.
By acknowledging the above-mentioned challenges and fostering communication between engineering and business teams, organizations can ensure their vulnerability prioritization process is effective, aligned with overall business goals, and leads to a more secure IT environment.
How to build a risk-based vulnerability prioritization model?
For vulnerability prioritization, a risk-based approach is very much essential for efficient resource allocation and effective threat mitigation. By focusing on and prioritizing the vulnerabilities that pose a great threat to the organization, security teams can maximize their impact and minimize the likelihood of a successful attack.
An effective vulnerability prioritization method that follows the basic principle mentioned above encompasses several key elements.
- Asset valuation: Determine the criticality of different assets based on factors such as financial impact, reputational damage, and regulatory compliance. This list can further vary from business to business.
- Threat assessment: Identify potential threats to the organization, including internal and external actors.
- Vulnerability assessment: Discover and categorize vulnerabilities within the IT infrastructure.
- Impact assessment: Evaluate the potential consequences of a successful exploit for each vulnerability.
- Likelihood assessment: Estimate the probability of exploiting a vulnerability based on factors like exploitability and attacker motivation.
- Risk calculation: Combine asset value, threat possibilities, and vulnerability impact to calculate an overall risk score.
Developing a risk-based prioritization model
Before developing a prioritization model, consider the above-mentioned qualitative challenges and implementation elements. Keeping them all in mind, you’re set to develop a prioritization model.
- Identify critical assets: Create a comprehensive inventory of assets, including systems, applications, data, and infrastructure components.
- Conduct threat assessments: Analyze potential threats to the organization, considering both internal and external factors.
- Perform vulnerability assessments: Utilize vulnerability scanning tools to identify weaknesses in systems and applications.
- Calculate risk scores: Assign risk scores to vulnerabilities based on factors like asset value, threat likelihood, and vulnerability severity.
- Prioritize vulnerabilities: Rank vulnerabilities based on risk scores, focusing on those with the highest potential impact.
- Continuously monitor and update: Regularly review and update the risk assessment model to reflect changes in the threat landscape and organizational priorities.
Prioritize vulnerabilities with Cloudanix
With a neat and easy-to-use dashboard, Cloudanix helps developers intuitively navigate to the findings while eliminating false positives. Cloudanix starts your security journey from code all the way to the cloud, including your vulnerability management until where it runs in your workload.
