What is Amazon EKS?
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) is a managed Kubernetes service by AWS that eliminates the need to install, operate, and maintain your own Kubernetes control plane or nodes. In simple terms, AWS handles the infrastructure and operational overhead, allowing you to focus on deploying and managing your containerized applications.
What is the Difference Between Kubernetes and EKS?
While Kubernetes is an open-source system to automate deployment, scaling, and operations of application containers, EKS is the managed version of Kubernetes offered by AWS.
Key Differences:
- Kubernetes: Self-managed by your organization.
- EKS: Fully managed by AWS with automatic control plane provisioning.
- High Availability: EKS spreads control plane across multiple Availability Zones.
- Security: EKS uses Amazon VPC network policies to isolate cluster traffic.
- Scalability: EKS handles scaling automatically; Kubernetes requires manual config.
Why Use Amazon EKS Over Regular Kubernetes?
Here are some key benefits of Amazon EKS:
- Usability: A single API and CLI interface to manage Kubernetes clusters.
- Reliability: No need to manually configure control plane components.
- Scalability: Automatically adjusts cluster size based on load.
- Integration with AWS Services: Easily integrates with ECR, ELB, IAM, CloudWatch, and more.
Watch This Video
Additional Features:
- Automatic Updates: Run secure, up-to-date versions of Kubernetes.
- Fargate Support: Run serverless containers with zero infrastructure management.
- Kubernetes Add-Ons: Built-in support for tools like Prometheus and Grafana.
Overall, Amazon EKS simplifies Kubernetes adoption while offering enterprise-grade security, scalability, and ease of use.
Components of Amazon EKS
Control Plane
Handles cluster management and includes:
- API Server: Entry point to interact with the cluster.
- Controller Manager: Manages cluster objects like pods, deployments, etc.
- etcd: A distributed key-value store for storing cluster state.
Worker Nodes
These are EC2 instances configured to run Kubernetes workloads.
Networking
Uses Amazon VPC to securely connect control plane and worker nodes and enable communication with internal and external services.
Best Practices for Amazon EKS Setup
- Allow inbound traffic only on Port 443 (HTTPS)
- Enable audit and activity logging
- Use the latest stable Kubernetes version
- Configure high availability across zones
- Make ECR repositories private
- Enable image tag immutability
- Attach lifecycle policies to ECR repositories
- Enable image vulnerability scanning for ECR
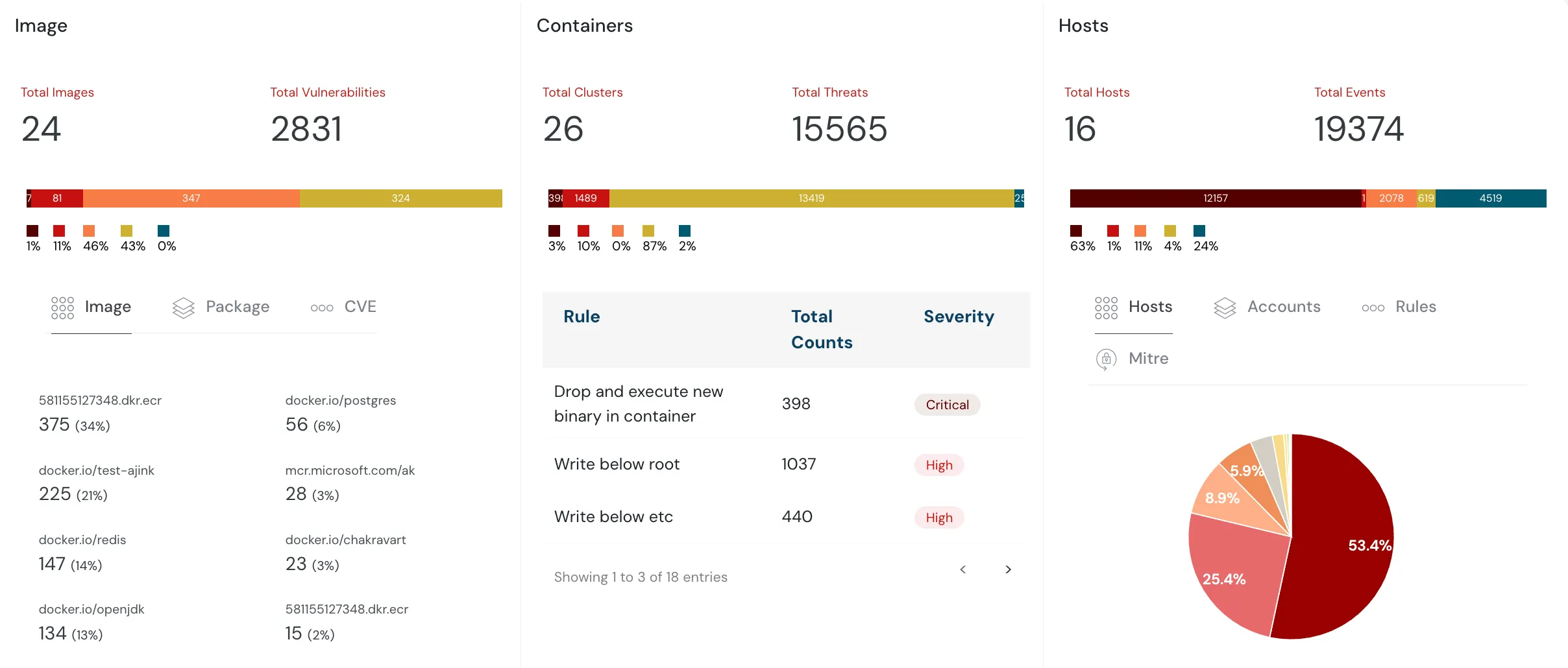
AWS EKS Audit with Cloudanix
Cloudanix provides curated Kubernetes audit checks and helps enforce best practices across:
- Amazon EKS
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Secure your containers with Cloudanix’s centralized dashboard and detect threats related to:
- IAM misconfigurations
- Workload exposure
- Vulnerabilities (like CVE-2022-0185)
- Compliance gaps across AWS, Azure, and GCP
Secure Your Containers With Cloudanix
