In today’s interconnected digital landscape, non-human identities have become the invisible backbone of modern IT infrastructure. While organizations have traditionally focused on securing human users, the exponential growth of machines, applications, and automated systems has created a new frontier of identity management that requires immediate attention.
Understanding What Is Non-Human Identities?
Identities managed and controlled by machines, not humans. Non-human identities are digital entities used to represent and authenticate machines, devices, and software applications within a computer system or network. Unlike human identities (which are typically associated with individuals), non-human identities represent widespread entities like Software programs, services, APIs, Servers, workstations, IoT devices, Scripts, bots, and other automated workflows and devices.
Three Key Characteristics of Non-Human Identity
Non-human identities are managed and controlled by machines, not humans. They often interact with systems and resources automatically, without direct human intervention. They are crucial for enabling various aspects of modern IT, such as cloud computing, automation, and machine-to-machine communication.
How Does Non-Human Identity Differ from Machine Identity?
We have seen industry experts often use these two terms interchangeably. Upon doing our study, we found that - While “non-human identity” and “machine identity” are often used interchangeably, there’s a subtle but important distinction:
Non-human identity is a broader term encompassing any entity that’s not a human user. This includes:
- Machines: Servers, workstations, IoT devices, etc.
- Applications: Software programs, services, APIs.
- Automated Processes: Scripts, bots, and other automated workflows.
Whereas Machine Identity specifically focuses on the identities of machines themselves. It deals with:
- Authenticating devices: Ensuring that a machine is truly what it claims to be.
- Securing machine-to-machine communication: Establishing trust between devices and enabling secure data exchange.
- Managing device certificates and keys: Issuing, managing, and revoking digital certificates used for machine authentication.
While the terms are often used interchangeably, understanding the nuances can help better understand the scope and challenges associated with securely managing these entities.
Why Do Organizations Need Non-Human Identities?
Non-human identities are essential components of modern IT infrastructure and cloud environments for several key reasons:
Resource Provisioning: Cloud platforms rely heavily on non-human identities for managing and accessing cloud resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and databases.
API Interactions: Non-human identities are essential for enabling secure and authenticated interactions between applications and cloud services through APIs.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Non-human identities are critical for automating software builds, testing, and deployments in CI/CD pipelines.
Service-to-Service Communication: In microservices architectures, non-human identities are used to authenticate and authorize communication between different services.
Increased Agility: Non-human identities facilitate rapid and agile development by enabling automated provisioning of resources and seamless integration with development tools.
In essence, non-human identities are the foundation of many modern IT practices, enabling automation, scalability, and agility while ensuring secure and controlled access to critical resources.
Learn More About NHI Management
What Are the Challenges of Non-Human Identities?
Experts in the industry often say “Humans are the weakest link”, but what about Non-Human Identities? We are sure you have the same question. Earlier, we felt there may not be any risks of having these non-human identities. But we were wrong, here’s what we found:
Credential Compromise
Compromised credentials associated with non-human identities (like API keys or service account passwords) can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems and data. This can lead to data breaches, service disruptions, and other serious consequences.
Lack of Visibility and Control
Organizations may lack visibility (Also known as blind spots) into the number and usage of non-human identities within their environment. This can create difficulty in managing and controlling access rights for a large number of non-human identities can lead to security gaps.
Over-privileged Accounts
Non-human identities are often granted excessive permissions, increasing the potential for misuse and abuse. Compromised accounts with overprivileged access can be used by attackers to move laterally within the network, gaining access to sensitive data and systems.
Supply Chain Risks
Organizations rely heavily on third-party software and services, which may introduce vulnerabilities through their own non-human identities. In case of an attack, malicious actors can compromise software components and introduce malicious code that can exploit non-human identities.
Difficulty in Detection
Unusual activity from non-human identities can be difficult to detect and distinguish from legitimate behavior, making it harder to identify and respond to security incidents.
These challenges highlight the importance of robust non-human identity management practices, including strong authentication, least privilege access control, regular audits, and continuous monitoring.
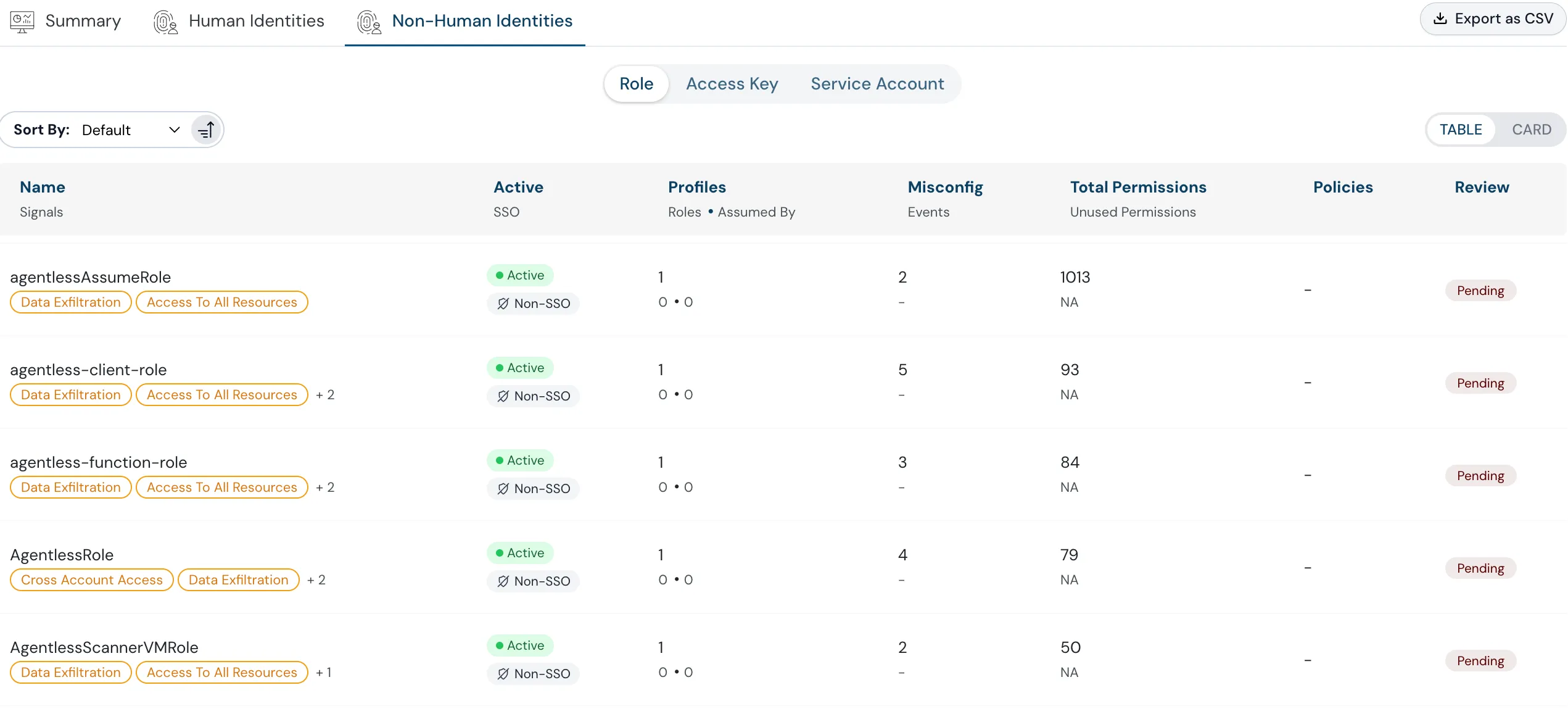
What Is Non-Human Identity Management?
Non-human identity management encompasses the processes and technologies used to securely manage and control the identities of machines, applications, and other non-human entities within an organization’s IT environment.
While sticking to the basics of identity management, we have tried to break the non-human identity management process down into 6 steps:
Inventory and Discovery
Identifying and cataloging all non-human identities within the organization. Understanding the purpose and usage of each identity.
Authentication and Authorization
Implementing secure authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of machines and applications. Defining and enforcing access control policies to ensure that non-human entities have only the necessary privileges to perform their functions.
Lifecycle Management
Managing the entire lifecycle of non-human identities, from creation and provisioning to deactivation and removal. Automating the creation, modification, and deactivation of identities as needed.
Security Monitoring and Auditing
Continuously monitoring the activity of non-human identities for suspicious behavior. Generating audit logs to track access requests, authentication attempts, and other relevant activities. Ensuring that non-human identities are right-sized (minimum permissions required) as we do the same for human identities.
Risk Management
Assessing and mitigating the risks associated with non-human identities, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and denial-of-service attacks. Automating the creation, modification, and deactivation of identities as needed.
Compliance
Ensuring that non-human identity management practices comply with relevant security standards and regulations.
Non-human identity management is critical for organizations to maintain a secure and efficient IT environment in today’s increasingly interconnected world. By effectively managing these identities, organizations can reduce the risk of cyberattacks, improve operational efficiency, and enhance their overall security posture.
What Are Some of the Effective Best Practices for Non-Human Identities?
We just took a look at the unique challenges that non-human identities present. You may ask us, can’t we do anything about it? You’ve got it answered. Here are some effective best practices for managing such NHI:
Principle of Least Privilege
Grant non-human identities only the absolute minimum permissions necessary to perform their functions. This significantly reduces the potential impact of a compromise. E.g. If an application only needs to read data from a database, grant it read-only access, not write or delete permissions.
Strong Authentication
Move beyond basic passwords. Implement strong authentication methods like digital certificates, short-lived API keys, and implement MFA where possible (even for non-human identities).
Automated Lifecycle Management
Automate the creation and provisioning of non-human identities based on defined policies and workflows. Automatically deactivate or revoke access for non-human identities when they are no longer needed. In addition to that, regularly review and update access permissions for all non-human identities.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Continuously monitor the activity of non-human identities for any suspicious behavior, such as unusual access patterns or high-volume requests. Analyze security logs to identify and investigate any potential threats or security incidents related to non-human identities.
Secure Storage and Handling of Credentials
Utilize secure methods for storing and managing sensitive credentials, such as API keys, passwords, and certificates. Avoid hardcoding credentials directly into applications. Use secure methods like environment variables or secrets management tools to store and retrieve credentials.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can effectively manage non-human identities, mitigate security risks, and ensure the secure and reliable operation of their IT systems.
What Are the Common Drivers of Non-Human Identities?
Understanding the drivers behind the proliferation of non-human identities is crucial. Here are some key factors:
Increased API Usage: Cloud computing relies heavily on APIs for interacting with services. This necessitates the creation of non-human identities (like service accounts or API keys) for applications to access cloud resources.
Automation and Orchestration: Cloud environments facilitate automation and orchestration through tools like Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC). These tools often utilize non-human identities to interact with cloud APIs and manage resources programmatically.
Service-to-Service Communication: Microservices architectures rely heavily on communication between different services. Non-human identities are essential for secure and authenticated communication between these services.
Automation: DevOps and CI/CD practices heavily rely on automation, with tools and scripts interacting with various systems and services. These tools require non-human identities to perform their functions.
AI/ML Systems: AI/ML models often interact with other systems and services, requiring non-human identities to access data, perform computations, and share results.
These factors have contributed to a significant increase in the number and complexity of non-human identities within modern IT environments. Effectively managing these identities is critical for ensuring the security.
Why Are Non-Human Identities the Biggest Blindspots?
Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, has emphasized that non-human identities are a significant blind spot for many organizations. This is because:
Lack of Visibility and Control: Organizations often lack visibility into the number and usage of non-human identities within their environment. This lack of awareness makes it difficult to identify and manage potential risks.
Focus on Human Identities: Traditional identity and access management (IAM) solutions primarily focus on managing human users, neglecting the critical need to secure and manage non-human identities.
Rapid Growth and Complexity: The rapid growth of cloud computing, microservices, and IoT has led to a proliferation of non-human identities, making it increasingly challenging for organizations to manage them effectively.
Gartner’s reports highlight the need for organizations to shift their focus beyond traditional human identity management and develop comprehensive strategies for managing non-human identities. This includes implementing dedicated tools and processes for discovering, managing, and securing these identities.
